Colposcopy Newport Beach, CA
Just got an abnormal pap smear test result and a referral for a colposcopy? Fret not. Our colposcopy facility in Newport Beach, CA has got you covered. We’re here to put your best interest first by providing you with a safe and re-assuring environment so your test is a success.
ORANGE COUNTY, NEWPORT BEACH
Colposcopy Test
Remember, this is not a cancer test but rather a diagnostic procedure that’s meant to study the nature of any irregular cells detected during a pap test. This allows for timely interventions and greater peace of mind for you in the long haul.
So, relax, you’re in safe hands. We are here to offer you the best experience possible before, during, and after the exam.
Why Choose Us?
We listen to you
At our practice, we prioritize your needs and take the time to fully understand any concerns you may have.
Our practice is for women and by women
As a women-centered practice, we are dedicated to providing care that is tailored to the unique needs of our female patients.
A warm, inviting, and reassuring environment
Our clinic is designed to create a welcoming and comforting atmosphere, ensuring that you feel at ease during your visit.
Our services are personalized to suit every patient’s unique needs
Our approach is client-centered, which means we put you at the center of all we do and our team will make you feel like family.
Targeted, minimally-invasive tests thanks to our state-of-the-art equipment
We utilize advanced technology and targeted, minimally-invasive testing methods to provide personalized care that is tailored to your individual needs.
We accept most insurance plans
Additionally, we accept a wide range of insurance plans, making it easier for you to receive the care you need.
Top-Class Care from The Best Colposcopy Experts in Newport Beach
At Broad Medical Group we understand that the referral for a colposcopy following an abnormal pap smear might leave even the strongest of us worried.
But it doesn’t have to be that way. With the best OB/GYN practice in Orange County at your service, your test is done seamlessly and in an unintrusive manner.
For most people, all it takes after the procedure is a bit of rest before they resume their normal day-to-day undertakings the following day.
Board-Certified Physician
We provide more than just a beautiful environment and the latest technology in the game. With years of experience and an outstanding track record, Dr. Jenifer Broad is at hand to ease your anxiety and provide you with the most considerate colposcopy services in Newport Beach area.
Dr. Broad is board-certified and passionate about women’s health. She leads a stellar team of nurses and assistants who equally share a genuine passion for female healthcare
Benefits of Having a Colposcopy Done at Our Orange County Practice
It’s perfectly normal to feel nervous when readying yourself for this kind of exam especially when you’re not sure what to expect. But whichever way you look at it, the merits of colposcopy heavily outweigh any demerits there might be.
This combined with our well-established in-house systems ensures that you get nothing but the best talent at your service each time you book an OB ultrasound appointment with us.
Benefits of Having a Colposcopy Done at Our Orange County Practice
This test allows for precise analysis of the cervix to help your doctor understand what exactly is behind your abnormal pap smear results. The good news is that most women with abnormal pap tests do not have cervical cancer. And the few who have it detected during the colposcopy examination can have it removed in-office and proceed with a normal life.
Should it happen that your colposcopy test results are unclear, a small sample tissue (a biopsy) may be taken from your cervix and taken to the lab for further examination.
1. It’s a Minimally Invasive Process
Thanks to our high-quality technology, we are able to keep the process minimally invasive. You’ll be required to sit on a comfortable chair and just like with the pap smear test, a speculum will be carefully inserted into your vulva to open it up.
Our board-certified physician will then use a special microscope with a light to examine your cervix.
It is important to note that your body will not be touched or stepped on in any way throughout this process.

2. A Good Way to Prevent Cervical Disease
As with any other medical condition, early and precise diagnoses lead to a greater likelihood of successful treatment.
Likewise, this diagnostic test can help in the early detection of any irregular cells that might be building up and have them removed in time.
The exam is actually all about accurately diagnosing any problem that might be bugging you in there and nipping it in the bud.
And usually, timely, professional interventions eventually make for lower costs of care as well.
3. Long-Term Health & Wellness
This test will enable us to understand what caused the abnormal pap test in the first place.
And armed with this information our board-certified physicians will be able to advise you on the best way forward.
A successful colposcopy can put to rest any concerns you might be having and this can, in turn, enhance your quality of life.
In addition, the procedure can help you understand your body better so you can take proactive measures to live a healthy and fulfilling life.
4. The Best Colposcope You'll Find Anywhere in The World
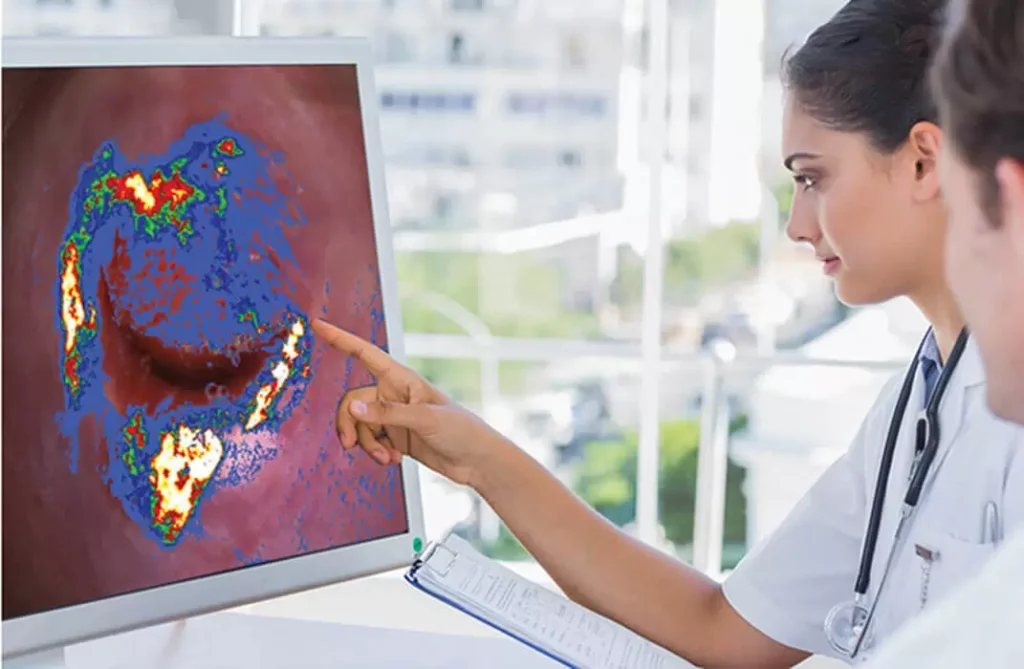
One thing that sets us head and shoulders above other practices is that we use the highly advanced DYSIS colposcope as opposed to the traditional colposcope.
Why does this matter? The DYSIS technology is light years ahead of the conventional imaging and diagnostic technology that dominated before. It is more accurate at capturing small-sized lesions that typically go unnoticed when low-grade diagnostic technology is used.
By generating high definition color-coded DYSIS maps, our experts are able to pinpoint any abnormalities and analyze them with greater confidence. This not only makes for a better first-time assessment but also helps you to understand your body better.
What Happens During the Test?
Before The Test
It is extremely important that your provider gets a clear view of your cervix during the test. Therefore, it is recommended to schedule this test when you’re not in your period.
Also, avoid using your tampons, douching, or inserting any medicine in your vagina during the 24 hours leading to your appointment. Inserting items into your vagina can cause irritation which can appear like abnormal cells during the test.
During The Test
Maximum care is taken to make the whole process comfortable so you can resume your normal life in the shortest time possible. The procedure lasts anywhere between 5-15 minutes.
If your gynecologist spots anything unusual on your cervix they will take a biopsy. This may cause some cramping or mild irritation but the discomfort usually goes away by the time the procedure is done.
After The Test
It is usually recommended to rest for the rest of the day. Most people are able to comfortably resume their daily activities the next day.
You are also advised to have another cervical exam test 6 months after treatment to check for abnormal cells and human papillomavirus (HPV).
If no HPV is found, you will not need to be tested again for 3 years. However, if HPV or significant cell changes are found, you will be referred for another colposcopy.
You may be advised to avoid the following after a colposcopy treatment:
- Driving or operating any machinery for at least 24 hours if your exam was done under general anesthesia.
- Usage of menstrual cups or tampons for at least 4 weeks (sanitary napkins may be recommended instead).
- Avoid sexual intercourse for at least 4 weeks
- Exercise for at least 2 weeks (this includes swimming)
Results of a colposcopy
It’s often possible to tell you right away if there are any abnormal cells in your cervix. But if you had a biopsy, it may take 4 to 8 weeks to get your results in the post. The result of the procedure and/or biopsy will be either:
Normal result

Normal – about 4 out of 10 people have no abnormal cells and are advised to continue going for cervical screening as usual
You will be advised to continue cervical cancer screening as usual, in case abnormal cells develop later.
Depending on your age, you will be invited for a cervical screening appointment in 3 or 5 years.
Abnormal result
Abnormal – about 6 in 10 people have abnormal cells in their cervix and may need treatment to remove them
The different types of abnormal biopsy results and their significance are as follows:
CIN 1 – the cells are unlikely to become cancerous and may go away on their own. No treatment is needed, and you will be invited for a cervical screening test in 12 months to check if they have disappeared.
CIN 2 – there is a moderate risk of the cells becoming cancerous, and treatment to remove them is usually recommended
CIN 3 – there is a high chance that the cells will become cancerous, and treatment to remove them is recommended
CGIN – there is a high chance that the cells will become cancerous, and treatment to remove them is recommended
Terminology
Your doctor or nurse may use the term CIN or CGIN when discussing your biopsy result. This is the medical term for abnormal cells. It is followed by a number (for example, CIN 1) that indicates the likelihood that the cells will become cancerous. A higher number means a higher risk of developing cancer if the cells are not removed.
Risks and side effects
The common side effects of the procedure are:
- mild pain, similar to menstrual pain – this should pass in a few hours and can be relieved with acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Mild vaginal bleeding and brown, watery vaginal discharge – this can last up to 4 weeks
There is also a small risk of more serious complications, such as:
- an infection – this can cause severe or persistent bleeding, smelly vaginal discharge, and persistent abdominal pain; see a doctor if you have these symptoms
- A slightly increased risk of premature birth (before 37 weeks of pregnancy) in future pregnancies – this is more likely if you need repeated treatments or a lot of tissue needs to be removed
In most cases, the benefits of treatment will outweigh these risks. Talk to a doctor or nurse if you have concerns or want to know more about the possible risks of treatment.
Utilizing DYSIS - The Next Generation Colposcope with an Advanced Cervical Scan.
DYSISmap is an adjunctive technology to assist colposcopy The DYSIS Colposcope is a high resolution digital colposcope with an adjunctive map. The DYSISmap is generated by a proprietary technology that measures the aceto-whitening reaction and summarises it in the form of an intuitive map. The DYSISmap is overlaid on the live image of the cervix to help with the identification of the most relevant biopsy sites.
A high resolution view of the cervix is presented on the touch-screen monitor. The image can be magnified and blue or green filters can be applied. Additionally, DYSIS has a High Contrast mode that is particularly useful to help with the identification of abnormal blood vessels or other morphological features.
The unique feature of the DYSIS Colposcope is that it accurately measures the reaction of the cervical epithelium using a proprietary technology called Dynamic Spectral Imaging. The results are summarised in the DYSISmap that is overlaid on the live image of the cervix. The inclusion of the DYSISmap information with the standard colposcopic indications can assist with the identification of cervical disease.
You can read more about DYSIS here: DYSIS Colposcope
Testimonial about DYSIS
DYSIS is an incredible addition to women’s healthcare. I have already identified areas of concern with the DYSIS mapping, which would have been overlooked with the naked eye. The standardization of the entire process gives me reassurance that there is enough acetic acid applied and enough time passed during the exam to get the best results. My patients are also much more at ease seeing what I see in real time.

Videos about DYSIS
Book your
Colposcopy Check-Up Today
Don't delay your reproductive health any longer, book your colposcopy check-up today and let our experienced and compassionate team provide you with the expert care you need for your well-being.
